In order to make full use of fertilizer labor and water resources, experts have developed integrated water and fertilizer technologies. This technology greatly improves water resource utilization by combining drip irrigation and fertilization. The following is a professional drip irrigation equipment manufacturer to introduce this technology to everyone.
1. What is the integrated water and fertilizer technology?

In a narrow sense, fertilizer is applied through an irrigation system, and crops absorb nutrients while absorbing water. Fertilization, which is usually performed at the same time as irrigation, is achieved by injecting a fertilizer solution into the irrigation water pipeline under pressure. The fertilizer-dissolved irrigation water is sprayed on the crops or dripped into the root zone through sprinklers (sprinklers, micro-sprinklers, drippers, etc.). Broadly speaking, it refers to the application after dissolving fertilizers, including spraying, pouring, spraying, and pipeline application.
2. What is the theoretical basis of integrated water and fertilizer technology?
The plant has two “mouths”, its roots are its large mouths, and its leaves are its small mouths. A large number of nutrients are absorbed through the root system. Foliar spraying can only supplement. How can the fertilizer we apply to the soil reach the plant’s mouth? There are usually two processes. One is called the diffusion process. After the fertilizer is dissolved, it enters the soil solution. The nutrients near the root surface are absorbed and the concentration decreases. The soil solution far from the root surface has a relatively high concentration. Another process is called mass flow. Under the condition of sunlight, the leaves of plants have open stomata and transpiration (this is a physiological phenomenon of plants), leading to water loss. The root system must continuously absorb water for leaf transpiration and water consumption. The water near the root system is absorbed, and the water in the distance will flow to the root surface, and the nutrients dissolved in the water will also reach the root surface and be absorbed by the root system. Therefore, the fertilizer must be dissolved in order to be absorbed, and the insoluble fertilizer plant “cannot eat” is ineffective. In practice, irrigation and fertilization are required at the same time (or integrated management of water and fertilizer), so that the fertilizer applied to the soil is fully absorbed, and the fertilizer utilization rate is greatly improved.
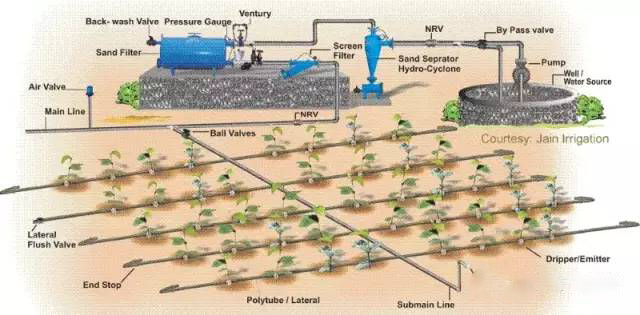
3. What are the common water and fertilizer integration measures?
The prerequisite for the integration of water and fertilizer is to dissolve the fertilizer first. It is then applied in a number of ways. Such as foliar spraying, overburdening and pouring, dragging pipe spraying, spray irrigation, micro-sprinkling irrigation (the most popular water spray in the south), drip irrigation, trunk injection and so on. Among them, drip irrigation application has the best effect because it prolongs the fertilization time and saves fertilizer.
4. What are the advantages of drip irrigation and fertilization?

Drip irrigation fertilization is an accurate fertilization method, which is only applied to the roots, which significantly improves fertilizer utilization. Compared with conventional fertilization, it can save more than 30-50% of the amount of fertilizer used. It can save a lot of fertilization labor and save more than 90% of traditional fertilization methods. Fertilization speed is fast, fertilization on an area of one thousand acres can be completed in one day; flexible, convenient and accurate control of fertilization time and quantity; significantly increase yield and quality, and enhance the ability of crops to withstand bad weather; can use marginal soil to grow crops, Such as sandy land, high mountain steep slope land, mild saline-alkali land, etc .; It is helpful to prevent fertilizers from leaching into the groundwater to pollute water bodies; It is beneficial to achieve standardized cultivation; Due to the coordination of water and fertilizer, the amount of water can be significantly reduced. In addition, the water-saving effect of facility irrigation itself can save water by more than 50%; drip irrigation and fertilization can reduce the spread of diseases, especially diseases transmitted with water, such as wilt. Because drip irrigation is single plant irrigation. During drip irrigation, water infiltrates into the soil and the ground is relatively dry, which reduces the inter-plant humidity and significantly reduces the incidence. Drip irrigation only moistens the root layer, there is no water and fertilizer supply between rows, and weed growth will be significantly reduced. Drip irrigation can drip pesticides, which has a better control effect on soil pests, nematodes and root diseases. The soil temperature is low in winter, the water can be heated and dripped to the root to increase the soil temperature. It has strong applicability in greenhouses. For thick and sticky soil, the drip irrigation pipe is buried in a certain soil depth, and the soil is air-filled by an air compressor to solve the problem of hypoxia at the root. Because drip irrigation is easy to achieve precise water and fertilizer regulation, in the case of deep soil layers, root systems can be introduced into the bottom of the soil to avoid high temperature damage to the root system in summer. Drip irrigation fertilization can be applied according to the crop’s need for fertilizer. Fertilize more when the amount is large, and fertilize less when the amount is less. Many crops are in the peak fertilizer period when they are closed, but people cannot enter the field and cannot topdress (such as potato, sugarcane, pineapple, etc.), while drip irrigation is not restricted and can be topdressed at any time. Due to the precise water and fertilizer supply, crops are growing fast and can enter the fruiting period or harvest early.





